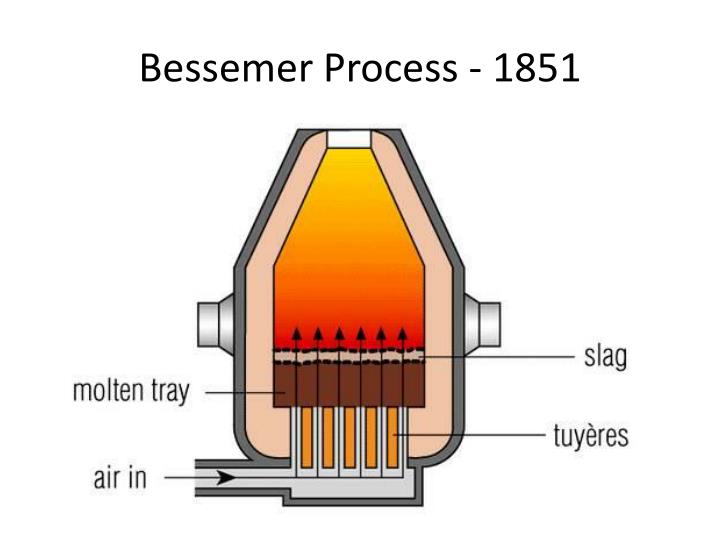
The process relies on the fact that oxygen from the air reacts with the carbon and other elements in the molten iron, burning them off and leaving a more. Bulk steel production was made possible by henry bessemer in 1855, when he obtained british patents for a pneumatic steelmaking process. (a similar process is said to have been used in the united states by william kelly in 1851, but it was not patented until 1857.) First, the steelmaker heats the iron in a furnace until it reaches a molten state, transforming it from solid to liquid form. The process is carried out in a large ovoid steel container lined with clay or dolomite called the bessemer converter.
The bessemer process, was the first inexpensive process for the. What it is and how it changed history. The process is carried out in a large ovoid steel container lined with clay or dolomite called the bessemer converter. Web the bessemer process is a way of steel production that uses a machine called a bessemer converter to produce steel cheaply.
The bessemer converter uses air to oxidize impurities in pig iron as well as control the amount of carbon in the iron. The bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. Web hidden away in the october 17, 1856 edition of the engineer, is the claim that henry bessemer was not the true inventor of the bessemer process.
The illustration accompanies text describing heavy metals and their commonly occurring compounds. The cooperation between science and technology proves to be a great success. Web the key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation through air being blown through the molten iron. Web bessemer converter, schematic diagram. Discover how injecting air into.
The process is carried out in a large ovoid steel container lined with clay or dolomite called the bessemer converter. Web phenomenon of the bessemer process and from that, draw conclusions. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten.
Web How The Bessemer Process Worked.
The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten. Air is blown into the furnace from the base and spiegel is. Web phenomenon of the bessemer process and from that, draw conclusions. Web within a decade the newly invented bessemer process would slash costs and massively increase production, changing the industrialised world forever.
The Bessemer Converters Are Introduced.
That was until 1856 when henry bessemer came up with a more effective way to introduce oxygen into molten iron to reduce the carbon content. Web in this video, we delve into the revolutionary bessemer process, a groundbreaking method that transformed the steel industry. Web bessemer converter, schematic diagram. Web steel was still unproven as a structural metal and production was slow and costly.
Web The Bessemer Process Was The First Inexpensive Industrial Process For The Mass Production Of Steel From Molten Pig Iron Before The Development Of The Open Hearth Furnace.
The key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. Web the bessemer process is a way of steel production that uses a machine called a bessemer converter to produce steel cheaply. Web a process for converting pig iron from a blast furnace into steel. 14k views 1 year ago furnace.
The Bessemer Process, Was The First Inexpensive Process For The.
What it is and how it changed history. The bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. Bessemer process first method for the mass production of steel. Web the bessemer's converter process explained.
The bessemer process, was the first inexpensive process for the. At this time the uk was the largest steel producer in the world, with the majority of the product being made in sheffield. Discover how injecting air into. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten. Web the key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation through air being blown through the molten iron.





/Bessemer-process01-3000-3x2gty-58b4e7c75f9b586046963aff.jpg)